In software development, if we need to choose a language for a project, we need to ask a few questions to ourselves before we make any decision.
For example what kind of project is it? scalability of the application, the complexity of the application, development budget, development time limit, application security, available resources, etc. The project team always wants the application to stay for the long haul and fulfilling the needs of the customer even if the business changes occur later on.
Knowing which type of mobile app you’re going to be developing is key in finding the right programming language.
Native App
When you create an app that uses a technology dedicated to one specific platform, like iOS or Android—that’s called a native app.
Each operating system has its own language used for coding a native app.
If you’re building an iOS native app, for example, you might want to use Objective C or Swift as the programming language.
For Android native app development, you would need to use Java or Kotlin.
Pros of Native App Development
Simpler code base and ecosystem results in faster performance
Functions well offline
Improved user experience due to platform-customized UI/UX components
Better security due to the various layers of protection of the operating system
Longer release cycles
Easier to prevent bugs and tech issues
Not dependant on third-party frameworks and libraries
Faster to build (since it’s for one specific platform)
Cons of Native App Development
Takes longer to develop for more than one operating system
Adding new features requires separate codebases
Since native programming languages are specific, you’ll need to hire a developer with that skill set
Everything has its pros and cons, and native app development is no different.
So who is this method of development best suited for?
Native app development is a good choice if you’re creating an app for one specific platform. It’s also a good choice if you want the best user experience by removing unnecessary features.
If you plan on creating a gaming app or an app that has heavy animations, native apps are the way to go since they can handle it due to faster performance.
Hybrid App
A hybrid app is a mix of native and web apps. It lets developers code in just one language which can be run on multiple operating systems.
You can use more well-known languages and frameworks when building a hybrid application, like JavaScript, HTML, and CSS.
When building this type of app, you would create your backend codebase which would then be covered in a native shell, allowing you to offer the app for both Android and iOS.
Pros of Hybrid App Development
Easier to develop, especially for multiple platforms
Since you’re using the same backend for all variants, there’s faster development time
Cheaper to develop for, since you don’t need developers specializing in specific languages
Easier maintenance due to hybrid apps being based on web solutions
Having one codebase makes it easier to add new updates and features
Can easily integrate with web-based services
Number of Active Developers Globally
Cons of Hybrid App Development
It’ll run slower if you have a complex, feature-heavy app
Relies on the security of your system browser
Having one codebase means the app runs equally on all platforms (instead of being coded to perform for a specific platform)
It’s a good idea to go with hybrid app development when you have a simple, content-based project that doesn’t involve heavy features and animations, or when you just want to get an MVP off the ground quickly.
PWA
Progressive web apps run in a web browser but still give users the look and feel of a native application.
So this means you can install the app on your mobile device—it works offline and can even —and you can still use hardware features like your GPS and camera.
Each platform is optimized and there are no limitations to what programming languages you can use.
Pros of PWA App Development
Accessible on various devices and platforms
PWA apps can be found in the browser
Faster loading speed
Ability to function offline
Cheaper to develop
Adapts well to various screen sizes (responsive)
Same look and feel of native apps
No installation process
Cons of PWA App Development
OS and hardware limitations
Hardware integration issues
Weaker performance on iOS
Not much support for iOS devices
Not available in app stores
If you want a low-cost and yet robust e-commerce app, PWA can be a good choice. Since it’s accessible on multiple devices and platforms, it’ll also result in higher traffic.
PRO TIP: Before jumping on what you think is the most popular mobile app programming language, take time to first think about which of these types of apps you plan on building.
What Programming Language Should One Learn?
The most important skill to learn in today’s world is to know how to write a computer program. Today, computers have entered in almost every industry. Be it the autopilot in an aircraft or digital speedometer in your bike, computers are omnipresent.
With programming and developer communities emerging at a rate faster than ever before, deciding on first programming language to learn can be a daunting task but one should consider the following factors while selecting the language to learn-
1) The job market for the language
2) The long term prospects for the language
3) How easy the language is to learn
4) What projects you can build while you’re learning (and share with friends so you can stay motivated)
5) What is the motivation behind learning the language(for fun or job)
Some of the popular options are-
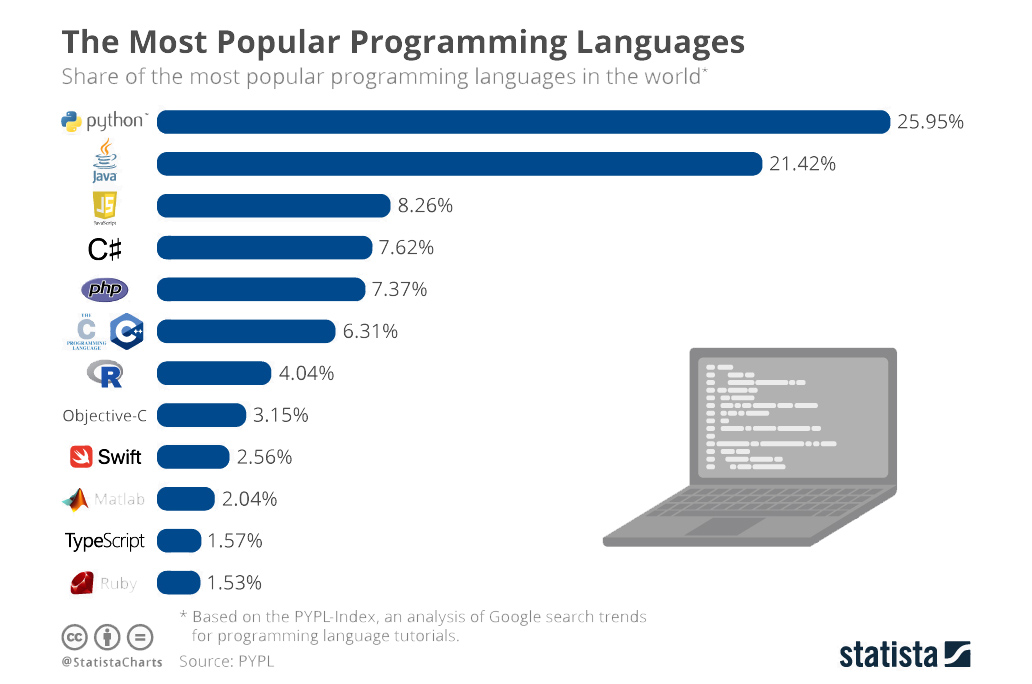
1) Python– It is widely accepted as the best programming language to learn first. It is a fast, easy-to-use, and easy-to-deploy programming language that is being widely used to develop scalable web applications. YouTube, Instagram, Pinterest, SurveyMonkey are all built-in Python.
2) Java– It is widely used for building enterprise-scale web applications. Java is known to be extremely stable and so, many large enterprises have adopted it. It is also widely used in Android App Development.
3) C/C++ is like the bread and butter of programming. Almost all low-level systems such as operating systems, file systems, etc are written in C/C++. If you wish to be a system-level programmer, C/C++ is the language you should learn.
4) Javascript– JavaScript is the “frontend” programming language. JavaScript is widely used to design interactive frontend applications. If you are looking for that cool tech job at your favorite startup, you should seriously consider learning JavaScript.
5) Go- Go, also known as Golang, is a programming language built by Google. Go provides excellent support for multithreading and so, it is being used by a lot of companies that rely heavily on distributed systems. Go is widely used in startups in Silicon Valley. However, it is yet to be adopted by Indian companies/startups. If you wish to join a Valley-based startup specializing in core systems, you should master Golang.
6) R programming language is one of the most commonly used programming languages for Data Analysis and Machine Learning. R provides an excellent framework and built-in libraries to develop powerful Machine Learning algorithms.Those who wish to join “Analytics” team of a large organization should definitely learn R.
7) Swift is the programming language that is used to develop iOS applications. iOS-based devices are becoming increasingly popular. Therefore, those who want to serve this ever growing community can learn Swift programming.
8) PHP is among the most popular backend programming language. Though PHP is facing tough competition from Python and JavaScript, the market still needs a large number of PHP developers. Those who wish to join a reasonably well old organization as a backend developer should aim to learn PHP programming.
9) C# is a general-purpose programming language developed by Microsoft. C# is widely used for backend programming, building games (using Unity), building Window mobile phone apps and lots of other use cases.
10) Matlab– MATLAB is a statistical analysis tool that is used in various industries for Data Analysis. MATLAB is used widely in the Computer Vision and Image processing industry as well.
11) Kotlin was announced as an official Android development language at Google I/O in May 2017. As of 2020, Kotlin is still most widely used on Android, with Google estimating that 70% of the top 1000 apps on the Play Store are written in Kotlin. Google itself has 60 apps written in Kotlin, including Maps and Drive.
In addition to its prominent use on Android, Kotlin is gaining traction in server-side development.
12) Rust– With direct access to hardware and memory, Rust is an ideal language for embedded and bare-metal development. You can write extremely low-level code, such as operating system kernels or microcontroller applications in rust.