Massive online marketplaces like Amazon and eBay are the first names that come to mind when discussing e-commerce. Given that Amazon has more total visits to its marketplace than any other US company, and eBay has more individual U.S. sellers than any other platform, these results should be no surprise.
An online marketplace where different businesses sell their goods and services is not a new idea, but how do you determine whether or not it is successful? The obvious solution is the revenue from the marketplace, which is dependent on the marketplace business model. To help you decide which business model is best for your company, we’ll discuss the common ones and their benefits and drawbacks.
What is a Marketplace Business Model
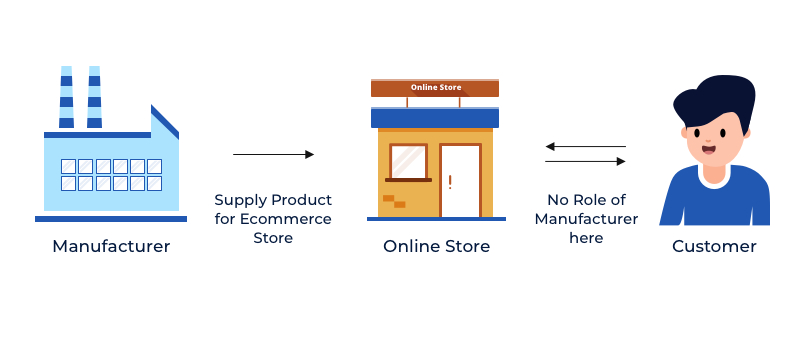
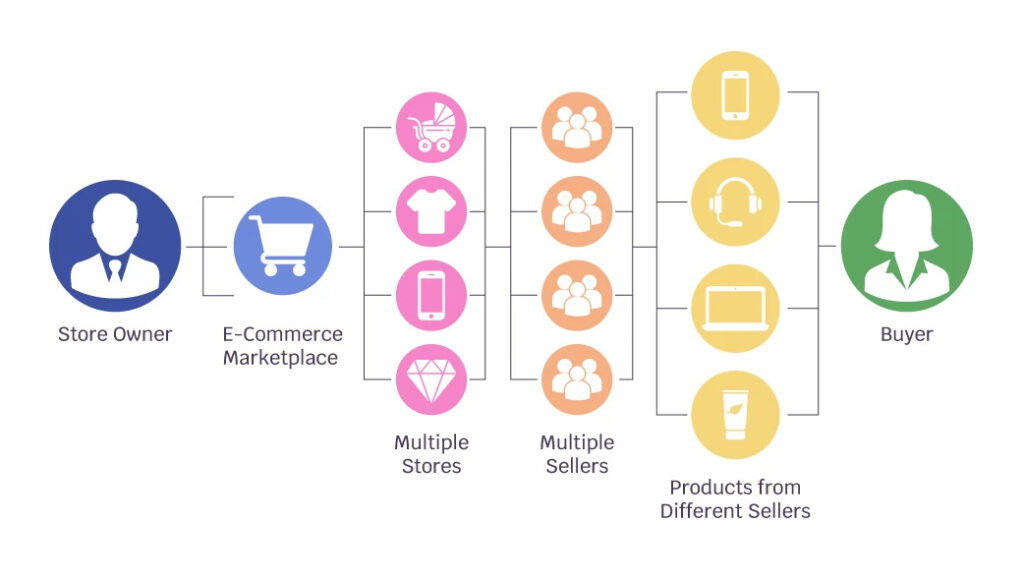
Online marketplaces aim to facilitate transactions between buyers and sellers through a unified and proprietary system. In many cases, the marketplace operator does not stock any goods but acts as a middleman between the buyers and sellers.
Their responsibilities could include ensuring everything goes smoothly with the logistics or helping with the finances. This frees up the sellers’ time and effort to concentrate on what they do best: satisfying the needs of their consumers with high-quality, personalized recommendations.
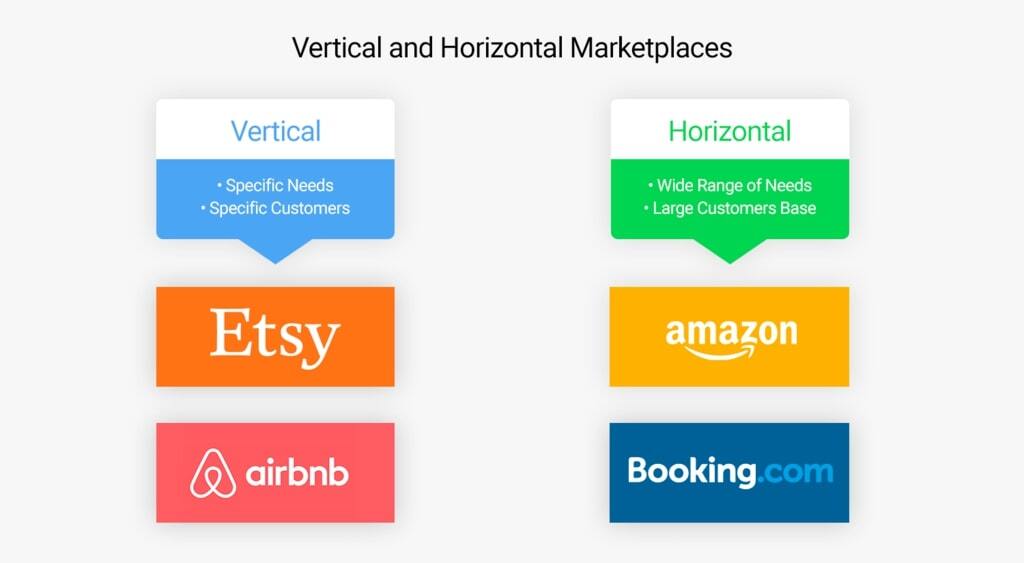
Although there is a wide variety of market structures, they can generally be categorized as horizontal or vertical.
Horizontal Marketplace Business Model
In a horizontal marketplace, customers can buy goods from various categories while receiving the same quality of service regardless of the category they shop in. For instance, eBay sells various goods, from apparel to electronics.
Vertical Marketplace Business Model
A vertical marketplace specializes in a single product type but provides a wide range of related services. StockX, a marketplace for sneakers, takes care of shipping, payment processing, and quality control. This enables them to act as reliable partners for potential customers.
Types of Marketplace Business Models
Offline Marketplace Model
An offline market’s business model and marketing strategy are determined by the consumers it serves. A retail store’s business plan is different from that of a flea market. Each person in a flea market can act as either a buyer or a seller. A retail store manager coordinates the efforts of several independent sellers who stock the store and sell their products there.
Online Marketplace Model
An online marketplace business model is the blueprint followed by internet marketplaces to draw in customers, keep the revenue flow, and keep up with the competition. There are operational costs, eCommerce accounting responsibilities, marketing approaches, and target users to consider.
There are several key differences between traditional marketplaces and their digital counterparts. First, shoppers’ expectations vary depending on whether they make an offline or online purchase. The consumer in a store knows they have to carry the item to their car. Customers who make purchases online have come to anticipate quick and cheap shipping and handling. These shopper behaviors shift accountability away from the buyer and onto the seller.
Two, online shoppers have access to a far wider variety of goods. There is no way to browse things other than what is in front of you at a brick-and-mortar store. You can easily switch to a different store in seconds when you shop online. So, you should sell at least a few popular items at reasonable prices.
Third, buyers have diverse product preferences when comparing online and traditional retail. Items such as clothing, technology, books, and toys are good for online sales. Products like mattresses, automobiles, swimwear, musical instruments, and furniture do better in offline stores because customers prefer to try them out in person. The best strategy is to adopt a marketplace business model tailored to your company’s specific niche.
Read more: Benefits Of A Mobile App In Every Business
Types of Online Marketplace Models
There are different types of Online Marketplace Models based on buyer-seller interactions.
Business-to-Business (B2B)
A business-to-business (B2B) marketplace is where two or more businesses can trade goods and services. The B2B concept and the processes that goods go through before they reach retail channels can be better understood by having a firm grasp of the wholesale supply chain. Make money in bulk purchases by advertising commonly purchased wholesale commodities and requiring a minimum order quantity (MOQ) from customers.
Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
The essence of electronic commerce is an online store where consumers may buy tangible goods. Entrepreneurs seek out (or create) high-demand products and then list and sell them online to their target demographics in the B2C Marketplace Model.
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
Any individual or group with goods to sell or a need to purchase goods can partake in this online marketplace. You must either post what you have for sale or utilize the search bar to locate what you are looking for. Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) sales are neither a business license nor other formal qualifications are required of the buyer nor the seller.
Key Metrics of the Marketplace Business Model
Many different types of markets exist. Businesses might have a business-to-business (B2B) or business-to-consumer (B2C) focus, serve a localized or global market, and have horizontal or vertical integration.
As a founder, how can you tell if you’re making the right decision? Part of the answer is to keep tabs on a handful of key metrics that will allow you to gauge your progress.
Customer Acquisition Cost
The Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) provides insight into how much it will cost to bring new customers and vendors into our platform. Marketing and sales expenses are added up and then divided by the total number of new customers to arrive at this figure.
For example, let’s say that we spend $2,000 on Facebook advertisements, which bring in 100 new customers. Our CAC would be $2,000 divided by 100 new customers, which would be $20. The objective is to reduce CAC as much as possible. The more money put into acquiring a user or merchant, the more value that user will need to provide on the platform before the investment is worthwhile.
Gross Merchandise Value
The gross merchandise value (GMV) reveals the overall value of all purchases. It’s determined by taking the average order value and multiplying it by the total number of transactions. Your platform’s gross merchandise value (GMV) would be 5 million if it enabled one million sales at an average price of USD 5. When calculating your GMV, be sure to deduct the cost of returns and cancellations for an accurate picture of your sales.
Average Order Value
The average order value (AOV) is calculated by dividing the total value of sales made on the platform by the number of sales made on the platform. If you make a million dollars in sales but only sell items of a ten-million-dollar value, your average sale is only ten dollars.
We can see how well we’re doing compared to the competition by looking at their average order value (AOV). Moreover, we can estimate the difficulty of luring customers to the market. As the price of a product or service rises, the percentage of potential buyers drops.
Liquidity
It is liquidity that fuels the economic engine that is our market. It is a measure of the level of activity in the market at any given time. Liquidity is evaluated by factors such as the number of buyers and sellers on the platform, the number of listings, and the number of transactions (both made and refunded).
The ultimate objective of any marketplace firm is to increase liquidity. Customer engagement increases as additional purchasing options are made available to them.
Repeat Purchases Rate
The percentage of your current clientele that has made a second purchase can be calculated using the repeat purchase rate. It is determined by dividing your total number of consumers by the number of customers who made at least two purchases.
Net Promoter Score
It’s calculated by asking respondents to rate their level of recommendation on a scale from 0 to 10.
Three groups can be identified by the score they give to the question.
- Promoters = score of 9 or 10 given
- Passives = score of 8 or 7 given
- Detractors = score of 0 to 7 given
The net promoter score (NPS) is determined by subtracting the percentage of customers who are promoters from those who are detractors.
The Chicken and Egg Marketplace Business Model Problem
There is some confusion among online marketplaces as to whether they should focus first on attracting sellers or buyers. The bigger the number of sellers, the more appealing the marketplace is to buyers. In turn, the quantity of customers is a crucial metric for sellers.
Various strategies can be used to bring in buyers and sellers in the marketplace business model.
How to Attract Buyers
A good way is to offer incentives to users who sign up for the service and/or make purchases. It could be a discount of 5%, 10%, 15%, or a predetermined dollar amount on a gift card.
Focus on easing as many problems as possible for your ideal customers by developing a top-notch solution that provides a satisfying experience. So, if your rivals aren’t resolving consumers’ payment issues, you can step in and do so by providing payment protection and a refund system.
How to Attract Sellers
Follow a methodical procedure. First, you must offer your items or services, establish your brand’s reputation, attract customers, and win their trust. If your platform has a dedicated consumer base, sellers flock to it.
Make a seller’s manual outlining the entire registration, listing, and selling procedure with detailed cost breakdowns. In addition, make a comprehensive summary of your platform, highlighting its many benefits.
How Marketplace Business Model Makes Money
Freemium Model
The freemium business model allows buyers and sellers to participate in the marketplace without incurring costs. Additional revenue can be generated through the sale of premium features or subscriptions or the upselling of complementary products and services.
This business strategy aims to catch consumers with a free service, so they have no choice but to pay for access to the full set of benefits your service offers. Finding a happy medium between free and paid offerings is difficult but necessary if you want users to stick around.
Subscription Model
With a subscription-based business model, buyers or sellers pay a regular fee to participate in the marketplace. Customers are enticed to buy because they stand to get access to a fantastic experience or save money. Conversely, retailers can attract customers who are more likely to make a purchase.
For a subscription model to work, the platform must be valued enough by users and merchants alike. You’d need a sizable user base to entice vendors to make a payment. If potential consumers don’t find an overall benefit to joining, they won’t sign up.
Ad placement
Featured advertising is typically found in markets that use a different business strategy, such as a commission or listing structure. In this case, the seller can pay more to have their listing featured higher in search results. The biggest problem is getting enough visits to the site so sellers will pay for these adverts.
Commission Model
The most common type of market structure is in which a commission is levied on each successful transaction. The platform owner then adds a price to the traded item or service, which might be either a flat rate or a percentage of the total.
Sellers can focus on providing excellent goods or services because the platform operator typically handles all financial and logistical operations. The strategy relies on the fact that anyone (both buyers and sellers) can sign up for the platform at no cost to either party. Any value created on the platform is returned to the marketplace operator.
Read more: How Can Entrepreneurs Make Money From Online Marketplaces?
Things to know before Marketplace App Development
It’s difficult to determine what online store or marketplace business model will work best for you. Even more challenging is getting people to adopt and work within the framework of the business model. As a newcomer to the field of e-commerce, your best chance of success will always rest on how effectively your business model fits in with your business process, target audiences, competencies, and available resources.
Users of a marketplace app can take advantage of several perks that are far more difficult to get or implement in traditional marketplaces. One of the main reasons marketplace apps are gaining popularity is that, unlike traditional businesses, the benefits outlined above apply to buyers and sellers. What’s more, marketplace apps have several other advantages that make them appealing, including:
Better exposure: sellers and buyers may find all the products they need in one convenient location, allowing for more product exposure without the need for supplementary vendor infrastructure or marketing expenditures.
More Sales: increased sales thanks to improved visibility and the elimination of the requirement to make investments in infrastructure; as a result, both the sales and their profit margins are much higher.
Improved User Experience: Because of the convenience of having everything only a click away, a well-designed marketplace app should provide a mobile experience that is quick, simple, and intuitive enough to make the user’s life easier.
Easy access to customer support: Most marketplace apps, Amazon, in particular, are known for their excellent customer service, which is far simpler to deliver on an online platform than in a face-to-face setting.
Marketplace apps level the playing field by providing small and independent enterprises with access to the same platforms, technology, and resources used by large corporations, giving them a competitive advantage.
Best Ecommerce Marketplace Ideas
Wholesale
With this type of business model, an e-commerce business owner can buy products in large quantities and at a discounted or wholesale rate. Originally, only business-to-business (B2B) transactions could benefit from this business method. However, with the advent of the internet and the subsequent expansion in the size and scope of the trading community, C2C and B2C sales have also adopted this method.
Online wholesale is growing at a rate that has surprised experts. For wholesale e-commerce, finding business partners through modern sales channels like cold calling, advertising agencies, trade shows, and influencer marketing takes a lot of work.
Private Label and White Label
These days, white-label commerce is a widespread way to do business. This is a marketplace business model in which the production of a product is outsourced to one firm while the promotion and distribution are handled by a different company. These days, many popular social media personalities make their living by engaging in this type of business, where they resell white-labeled products to their followers.
Private labeling is also a great option for those dealers because it allows them to brand their products whatever they like. Here, they can place bulk orders with a certain manufacturer, receive the products secretly, and rebrand them under their name before selling them.
Print-on-Demand Online stores
T-shirts, sweatshirts, mugs, photo frames, phone cases, canvases, and other products bearing personalized designs are the most popular items in this category. When a consumer orders one of these goods, the item is sent to a third-party printing manufacturer, where the design selected by the customer is printed in high quality before being expertly packaged with brand logos and shipped directly to the customer.
It shares many of the same advantages of dropshipping, such as low overhead costs and a low potential for capital loss.
Dropshipping
This strategy allows companies to sell and market their items online without stocking inventory, even if they start with little money. After receiving an order from a customer, the company purchases the product from the supplier and immediately ships it out to the customer.
Pros and Cons of the Marketplace Business Model
Advantages
Extremely profitable. High-profit margins are possible if a marketplace achieves market dominance (and so reduces its advertising costs). When customers recognize your store as their go-to, the amount you have to spend to get them to make purchases drops dramatically.
Active participation from the user base. High levels of user engagement are common in e-commerce marketplaces that cater to repeat buyers. Customers may be enticed to explore the market in search of bargains or new stores because of the marketplace’s emphasis on communication and discovery. However, vendors are competitive by nature and, to that end, conduct significant market research.
Once the foundation of the network has been established, users are most likely to stick to the system. To catch up to you, your rivals would need to develop superior products and brands and a distribution network on par with yours. Putting up the effort here is not only time-consuming but also quite expensive. For this reason, dominant markets already established themselves are notoriously difficult to displace.
Disadvantages
Seller quality varies widely. There may be a wide range in price and quality between different vendors. This might become a major issue when sellers are also responsible for logistics like shipping. Operators of online marketplaces need to consider this and put resources into their seller platform. That means ensuring products and sellers are real or building a logistics network to make transportation easier.
A high initial investment is required. It can be expensive to launch a marketplace due to the time and effort required to build the required technology stack, promote the platform to attract buyers and sellers, and staff the business with qualified individuals. Building a sizable cash stream could be a time- and resource-consuming process that requires significant commitment.
Intense levels of rivalry are commonplace in marketplaces because of the potential for high profits they might generate. Although it might be expensive to launch a marketplace, more and more backers are prepared to provide capital to help new businesses stay competitive.
Successful Marketplace Business Models Revisited
Amazon Marketplace Business Model
To complement its product offerings, Amazon also hosts those independent sellers. Amazon has two different options for sellers. The first is geared toward people who have little interest in marketing or using sophisticated sales techniques. Each item sold on the platform incurs a $0.99 commission fee, with a monthly cap of 40 products sold. The monthly price for professional sellers is $39.99 (not including expenses for listing and selling extra items).
Due to the model’s reliance on a customer base willing to pay for the marketplace’s services, it can guarantee a steady and reliable stream of revenue. The favorable terms will allow you to attract more customers. Users pay a nominal fee monthly and can cancel at any moment.
eBay Marketplace Business Model
EBay listing is free to create; however, premium ad placement is available for a price. eBay’s marketplace business model is a hybrid, with one model as the primary revenue generator and the others providing supplemental income. When multiple revenue streams are utilized, the marketplace can generate more money.
Airbnb Business Model
Airbnb connects those looking to host with those looking to travel. People with extra space in their homes can rent them out to travelers, and those who stay there will pay the hosts a fee. Profits for Airbnb come from both listing and guest fees. Airbnb’s business model provides a platform for these listings and bookings. There are two primary ways in which Airbnb generates income:
Airbnb charges hosts a 10% service fee for each confirmed reservation made through their platform. This is a part of Airbnb’s overall pricing structure. Travelers will also be charged a 3% transaction fee when they pay for their accommodations online.
Conclusion
Building a solid foundation for your business is typically more intense than you might expect at first. A deep awareness of both your consumers and your competitors is required, in addition to filling out paperwork and saving money for expenses.
Your company’s success depends on making the best choice for your marketplace business model, which should be based on your specific demands and objectives. Your newfound knowledge of running a business effectively will allow you to get your venture off the ground in a favourable setting.